Pigmentation
Understanding and Treating Pigmentation
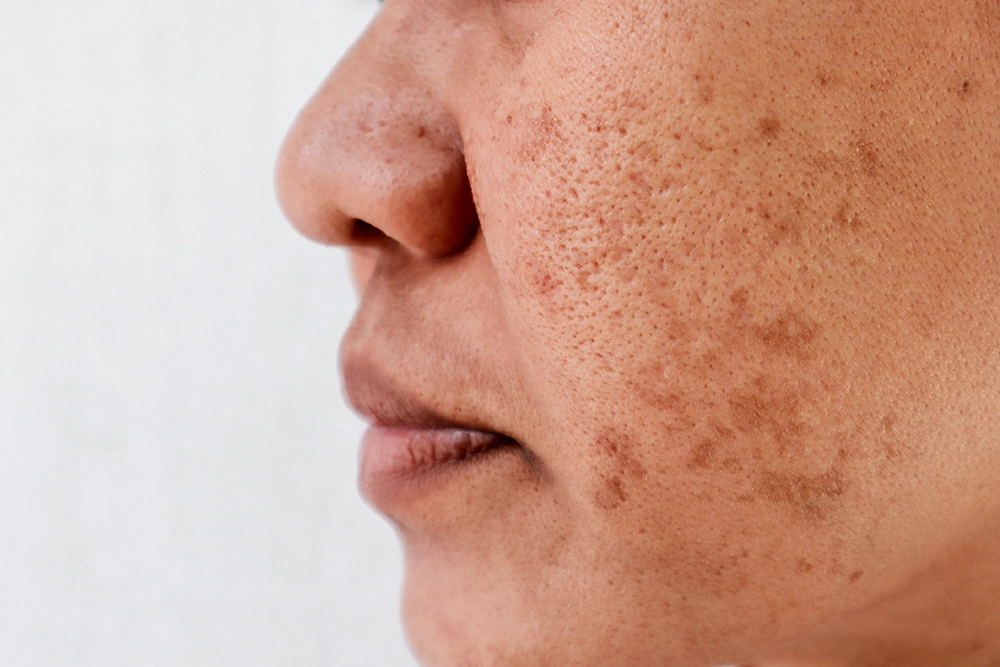
Pigmentation, whether it’s sunspots, melasma or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, often affects people’s self-esteem and confidence. To manage this condition, you would need to understand the causes and see what treatment works for you.
What is Skin Pigmentation?
Melanin and its Role
Melanin is a pigment produced by specialised cells called melanocytes, located in the epidermis (the outermost layer of the skin). Its primary function is to protect the skin from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. When skin is exposed to sunlight, melanocytes produce more melanin, leading to tanning. However, an overproduction or uneven distribution of melanin can result in hyperpigmentation, while a lack of melanin can cause hypopigmentation.
There are two main types of melanin:
- Eumelanin: This type produces brown and black pigments and is more prevalent in individuals with darker skin tones.
- Pheomelanin: This type produces red and yellow pigments and is more common in individuals with lighter skin tones.
The ratio of eumelanin to pheomelanin, along with the overall amount of melanin, determines an individual’s skin color.
Common Types of Pigmentation
Several types of pigmentation disorders can affect the skin, each with its own distinct characteristics and causes:
- Sunspots (Solar Lentigines): These are small, flat, darkened patches that appear on areas of the skin frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, and arms. They are a result of cumulative sun exposure over time.
- Melasma: This condition is characterized by brown or gray-brown patches, typically on the face, particularly the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. Melasma is often triggered by hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or the use of oral contraceptives.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): PIH occurs as a result of inflammation or injury to the skin, such as acne, eczema, psoriasis, or cuts and burns. It manifests as darkened spots or patches in the affected area.
- Freckles (Ephelides): These are small, flat, brown spots that appear on sun-exposed skin, particularly in individuals with fair skin and red hair. Freckles are caused by increased melanin production in response to sunlight.
- Age Spots (Seborrheic Keratoses): These are raised, waxy, brown or black growths that typically appear on the face, chest, shoulders, or back. They are more common in older adults and are not caused by sun exposure.
Causes of Pigmentation
Several factors can contribute to the development of pigmentation disorders:
Sun Exposure
Hormonal Changes (Melasma)
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Genetics
Treatment Options for Pigmentation
If you’re struggling with pigmentation, you can consider a variety of treatment options, ranging from topical creams and serums to advanced procedures like chemical peels and laser treatments. The best approach depends on the type and severity of pigmentation, as well as individual skin characteristics and preferences.
Topical Treatments (Creams, Serums)
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against pigmentation. These products contain active ingredients that help to lighten dark spots, inhibit melanin production, and promote skin cell turnover. Some common ingredients found in topical treatments for pigmentation include:
- Hydroquinone: A potent skin-lightening agent that inhibits the enzyme tyrosinase, which is essential for melanin production. Hydroquinone is available in prescription and over-the-counter formulations.
- Retinoids: Derivatives of vitamin A that promote skin cell turnover, reduce melanin production, and improve skin texture. Retinoids are available in various strengths, including prescription-strength tretinoin and over-the-counter retinol.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that helps to brighten the skin, reduce inflammation, and protect against sun damage. Vitamin C also inhibits melanin production.
- Azelaic Acid: An acid that helps to lighten dark spots, reduce inflammation, and kill acne-causing bacteria. Azelaic acid is effective for treating PIH and melasma.
- Kojic Acid: A natural skin-lightening agent derived from fungi. Kojic acid inhibits tyrosinase activity and helps to reduce melanin production.
- Niacinamide: A form of vitamin B3 that helps to reduce inflammation, improve skin barrier function, and lighten dark spots. Niacinamide is well-tolerated by most skin types.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, which exfoliates the outer layers and promotes new skin cell growth. Chemical peels can effectively reduce pigmentation by removing damaged skin cells and stimulating collagen production.
- Superficial Peels: These peels use mild acids, such as alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs), to exfoliate the outermost layer of the skin. Superficial peels are effective for treating mild pigmentation, such as sunspots and PIH.
- Medium-Depth Peels: These peels use stronger acids, such as trichloroacetic acid (TCA), to penetrate deeper into the skin. Medium-depth peels are effective for treating more severe pigmentation, such as melasma and deeper sun damage.
- Deep Peels: These peels use the strongest acids, such as phenol, to penetrate the deepest layers of the skin. Deep peels are used to treat severe pigmentation, deep wrinkles, and scars. Deep peels require significant downtime and are associated with a higher risk of complications.
Laser Treatments
Laser treatments use focused beams of light to target and break down melanin in the skin. Laser treatments can effectively reduce pigmentation by selectively destroying pigmented cells without damaging the surrounding tissue. Different types of lasers are used to treat pigmentation, including:
- Q-Switched Lasers: These lasers deliver short bursts of energy that shatter melanin into smaller particles, which are then eliminated by the body. Q-switched lasers are effective for treating sunspots, freckles, and PIH.
- Fractional Lasers: These lasers deliver energy in tiny columns, leaving surrounding tissue intact. Fractional lasers stimulate collagen production and improve skin texture, while also reducing pigmentation.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive procedure that uses a special device to exfoliate the outer layer of the skin. Microdermabrasion can help to reduce mild pigmentation by removing dead skin cells and promoting cell turnover. It is often used in combination with other treatments, such as topical creams and chemical peels.
Preventing Pigmentation
Preventing pigmentation is often easier than treating it. By adopting a proactive approach to skincare and sun protection, you can minimise your risk of developing pigmentation disorders.
Sun Protection (Sunscreen, Protective Clothing)
Avoiding Irritants
Proper Skincare Routine
Choosing the Right Pigmentation Treatment for Your Skin
A doctor would be best placed to help you decide what treatment works for you. Here are some general points you can keep in mind, though, ahead of your consultation.
- Skin Type: Different skin types respond differently to various treatments. For example, individuals with sensitive skin may need to avoid harsh chemicals or aggressive procedures.
- Type of Pigmentation: Some treatments are more effective for certain types of pigmentation than others. For example, laser treatments may be more effective for sunspots, while topical creams may be more effective for melasma.
- Severity of Pigmentation: Mild pigmentation may respond well to topical treatments, while more severe pigmentation may require more aggressive procedures, such as chemical peels or laser treatments.
Get Pigmentation Treatment
At DermClear, we understand the impact that pigmentation can have on your well-being. We have years of experience helping people with this condition and are committed to providing personalised solutions to patients.
We offer a range of treatments, from topical to laser solutions. Consult us today for a tailored treatment plan!
Sculpt the Body You Want–Feel Confident in Your Skin
Our friendly team is looking forward to serving you. For urgent enquiries and appointment requests, please call the clinic directly.